Medical Peel
Medical peel
Skin peel is a safe and non-invasive procedure to improve various skin conditions which can be done in a few minutes. Peel is one of the most commonly performed medical aesthetic procedures which can be used for a multitude of skin conditions.
Peel is the controlled removal of the layers of the skin using special chemicals following which regeneration and remodeling occur. The depth of action depends on the type of chemical peel, the number of layers of peel applied to the skin, and the duration to which chemical peel is applied for.
HISTORY OF PEEL
Peel has been used in various forms for centuries with ancient Egyptians were using it to maintain their beauty and youth over 2000 years back.
Since then peel has come a long way in regards to its safety and effectiveness.

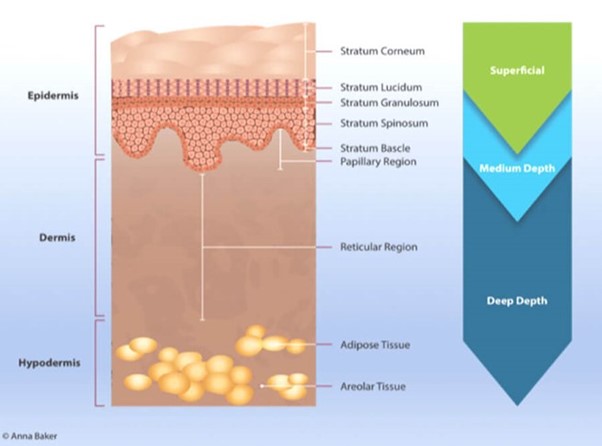
TYPES OF PEEL
The objective of the peel is to cause destruction at the required depth without scarring. Thus, Categorised according to depth :
- Very superficial
- Superficial
- Medium depth
- Deep peels
As explained before, the penetration of peel varies from peel to peel as well as the concentration of chemicals used even if peels have the same ingredients.
WHO CAN HAVE PEELS?
Peels can be used by any age group for a variety of skin conditions, not limited to, listed below:
– Photo damaged skin
– Actinic keratosis, early thin seborrheic keratosis
– Ichthyosis – thickened scaling skin
– Keratosis pilaris
– Hyperpigmentation (e.g. solar lentigines, melasma, PIH, age spots)
– Acne – atrophic scars, enlarged pores, excess sebum
– Acne rosacea
– Pseudofolliculitis barbae
– Fine lines and wrinkles
Any person from any age and ethnic background can have peels but darker skin types have to be careful in regards to the development of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) after the peel. Risk can be minimized by using proper pre-and post-care products.
There are some contra-indications to chemical peels listed below:
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding
- Active infection, open wound or inflammation in the treatment area (e.g., herpes simplex or cellulitis)
- Dermatoses such as vitiligo and active psoriasis, seborrheic or atopic dermatitis in the treatment area
- History of keloid or hypertrophic scar formation
- Impaired healing (e.g., due to immunosuppression)
- Isotretinoin (Roaccutane) use within the past 6 months
- Sunburn or recent sun exposure
- skin cancers over treating area
- Allergy (e.g. salicylic acid is a derivative of aspirin)
- Obsessive picker
- Severe redness associated with conditions such as rosacea, telangiectasia, poikiloderma of Civatte
- Uncontrolled serious medical condition
Thus the doctor will assess you before recommending the chemical peel for your skin condition. Kindly feel free to ask questions during the consultations
WHAT TO EXPECT?
Peel procedure is well tolerated and you can go about your daily activities immediately after the procedure, however, after the peel you might have mild irritation and redness. If deeper peels are used it can cause some exfoliation. Also, avoidance of sun exposure and applying sunscreen immediately after the procedure is required.
AFTER TREATMENT
- You may need to keep cooling your skin for a few minutes or more depending on the skin condition and the type of the peel.
- You can opt to undertake LED treatment immediately after the peel
- Do not rub the skin.
- Use sunscreen; mask; hat/umbrella to minimize the sun exposure
- You may need several sessions to achieve the most appealing result.
